Access Hakyll website on LAN and iptables
Posted on October 2, 2012
Tags: hacksoft
Hakyll Setup Series
- Setup Mathjax
- Setup PlantUML
- Setup autobuild Hakyll site Git action CI
- Very Simple Hakyll Pandoc Filtering Example
- Add Railroad Syntax to Hakyll
- Table Of Content in Hakyll
- Hakyll Access on LAN server
1 Scenario
- Hakyll server:
listening on 127.0.0.1 port 8000...
- Client in LAN: must hit 192.168.1.245 port 8000 to see the website
Client goes to http://192.168.1.245:8000 but sees ERROR
- Hakyll server: 127.0.0.1 in port 8000 cant be seen in LAN
GOAL Hakyll server: must open 127.0.0.1 port 8000 for LAN
2 Solution
2.1 Solution 1
stack exec -- site watch --host "0.0.0.0"alternatively use a Makefile
run:
stack exec -- site watch --host "0.0.0.0"
build:
stack exec site build
stbuild: build
./stork-ubuntu-20-04 build --input "./docs/searchindex.toml" --output "./docs/storksearch.st"
stbuildrhel: build
./stork-amazon-linux build --input "./docs/searchindex.toml" --output "./docs/storksearch.st"to run hakyll
make run2.2 Solution 2
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.route_localnet=1
sudo iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -p tcp -d 192.168.1.0/24 --dport 8000 -j DNAT --to-destination 127.0.0.1:8000#list nat table rules
sudo iptables -t nat -L --line-numbers#get nat table, select PREROUTING chain, delete number 2
sudo iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING 2-j DNATmeans rewriting Destination Network Address Translation aka IP rewriting.- if any site is trying to connect to “192.168.1.245:8000”(
-p tcp -d 192.168.1.0/24 --dport 8000),
it will translate that address to “127.0.0.1:8000”(-j DNAT --to-destination 127.0.0.1:8000)
3 Theory
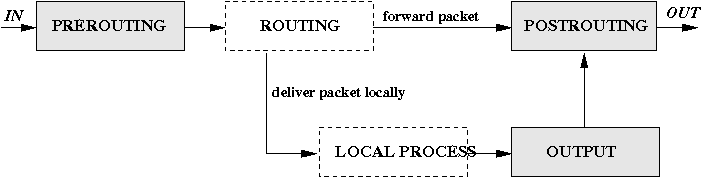
iptables -t filter ..is default table w/ INPUT, FORWARD, OUTPUT- FORWARD chain is typically useless, it’s when packets isnt directed towards you but passes through you like most router packets.
iptables -t nat ..w/ PREROUTING, OUTPUT, POSTROUTING
4 iptables netstat diagnosis
sudo iptables --append INPUT --source 1.2.3.4 --jump DROP
sudo iptables --list
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
DROP all -- 1.2.3.4 anywhere- says append a rule to the INPUT chain and if a packet matches source 1.2.3.4 then DROP it
- INPUT chain means all packets coming to the server is affected by this rule
4.1 netstat
sudo netstat -lnp
#tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8787 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 734/rserver
#tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:8000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 149480/myblog 4.2 iptables
sudo iptables -L### list INPUT rules
sudo iptables -L INPUT --line-numbers
### delete rule 2
sudo iptables -D INPUT 24.3 Rate limiting
- Rate limiting is not possible with vanilla iptables because it ratelimiting requires stateful connections
- A hashmap maps “ConnectionSrc-ConnectionDst” to {“NEW”,“ESTABLISHED”,…}
- Using Connection state to rate limit
5 Occupied port scenario
Say you launch a server to listen on port 8000
but ERROR: port 8000 being used
first check what process is running on port 8000
sudo netstat -lnpnext check what the parent process is
ps -aef --forest #outputs PID ParentPID treeterminate the process or it’s parent
kill -9 <PID>