Learn C
Posted on July 1, 2014
Tags: c
Code are commented to match with diagram
1 Pointers
1.1 Simple
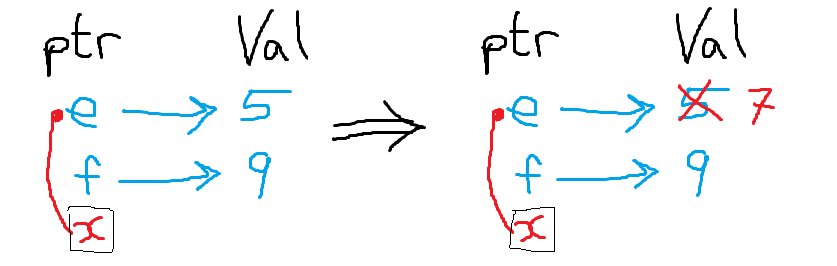
int main(){
int e = 5;
int f = 9;
int *x;
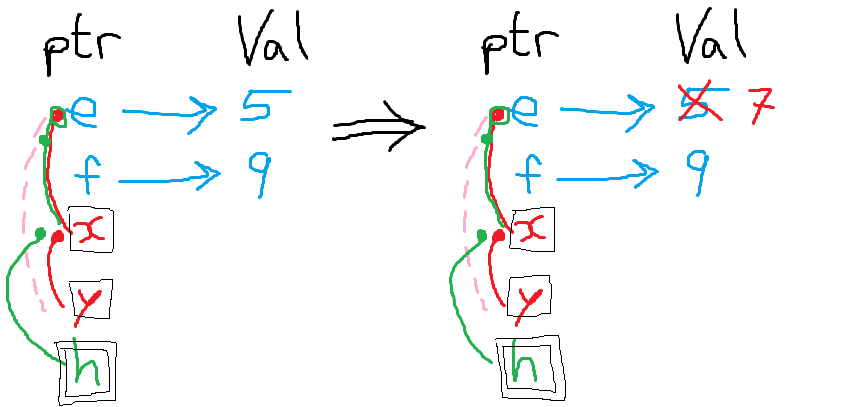
x = &e; //red arrow from x to e
*x = 7;
printf("%d",e); //outputs 7
}1.2 Point to same Value
- The red arrow is forcibly composable.
- Meaning if we have 2 red arrows, we must compose them.
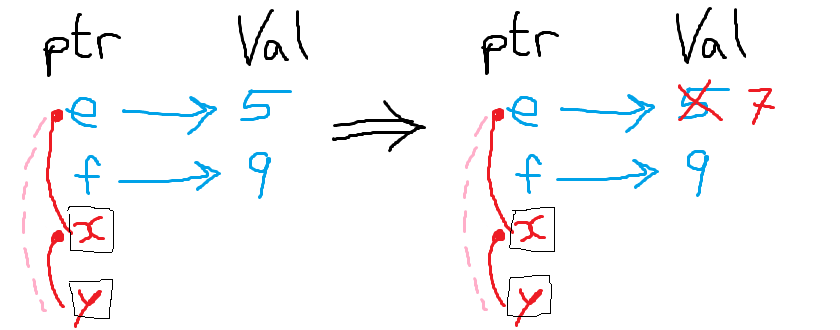
int main(){
int e = 5;
int f = 9;
int *x;
int *y;
x = &e; //red arrow from x -> e
y = x; //pink arrow via forcibly composed red arrows: y -> x, x -> e
*y = 7;
printf("%d",e);
}1.3 Change Value via Pointer Deref
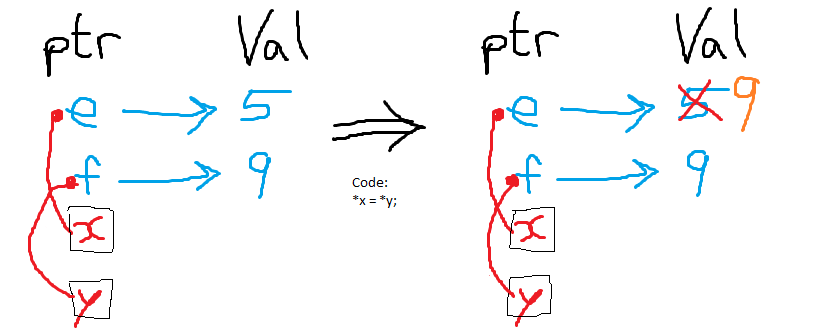
int main(){
int e = 5;
int f = 9;
int *x;
int *y;
x = &e; //red arrow from x to e
y = &f; //red arrow from y to f
*x = *y; //Change values from 5 to 9
printf("%d",*x);
}1.4 Swap
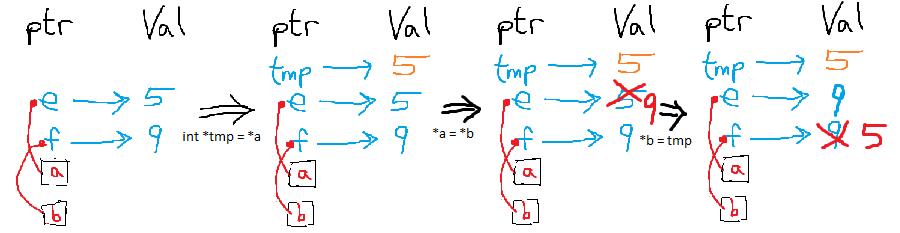
void swap(int *a, int *b){
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
int main(){
int e = 5;
int f = 9;
swap(&e,&f);
printf("%d",e); //9
}1.5 Nested Pointer
- Double pointer
int **hgets 2 green arrows- First green arrow points to x
- Second green arrow Binds to the x’s red arrow
int main(){
int s[5] = {4,3,2};
int e = 5;
int f = 9;
int *x;
int *y;
int **h;
x = &e; //red arrow from x to e
y = x; //red arrow from y to x
h = &x; //first green arrow
**h = 7; //second green arrow
printf("%d",e); //outputs 7